What are tools?
Language models excel at text generation but struggle with tasks like calculations, data retrieval, or interacting with external systems. To make an analogy, these models have impressive brains or reasoning capabilities, but lack the hands to interact with the digital world.
To solve this, many AI models support calling (sometimes referred to as ‘function calling’).
The use case for tool-calling
Say a colleague shares a document with you on Google Drive, and you’d like an LLM to help you analyze it.
You could go to your Drive/Docs, open the document, copy its contents, and paste it into your chat. But what if the LLM could do this for you? The Arcade Google Docs Server provides a SearchAndRetrieveDocuments . By calling it, the LLM can find and read the document without you having to do anything.
After analyzing the document, you decide that a meeting is needed with your colleague. You can ask the LLM to schedule a meeting and it will use the Google Calendar MCP Server to do it without you needing to leave the chat.
Or you could ask the LLM to send a summary of the analysis to your colleague by email and it would use the Gmail MCP Server for that.
Possibilities for Application and AI Agent developers
-calling combines the reasoning power of LLMs with virtually any action available through APIs or code execution.
With the Arcade SDKs, it is easy to build applications and AI that can leverage -calling in order to provide an LLM-powered experience to in a secure and privacy-forward way.
How tool calling works
AI models that support calling can determine when and how to use specific tools to fulfill a ’s request. The developer decides which tools to make available to the model, whether existing tools or tools they’ve built themselves.
In the example above, when the asks: “help me analyze the ‘ XYZ’ Google document shared by John”, the LLM can use its reasoning capabilities to:
- Recognize that it needs to access external data;
- Evaluate that the
GoogleDocs.SearchAndRetrieveDocumentsis the best way to get that data; - Call the with the appropriate parameters;
- Read the document content and use it to answer the ’s questions.
The authorization problem
One challenge to make all that happen is authorization. How do you give the LLM permission to access someone’s Google Docs and Gmail in a secure and convenient way?
Arcade solves this problem by providing a standardized interface for authorization, as well as pre-built integrations with popular services such as Google, Dropbox, GitHub, Notion, and many more.
Our SDK also allows you to integrate LLMs with any OAuth 2.0-compliant API.
Tool Augmented Generation (TAG)
Similar to Retrieval Augmented Generation (RAG), calling allows the AI to use external data to answer questions. Unlike RAG, tool calling is more flexible and allows the AI to use tools that are much more diverse than text or vector search alone.
The following is a diagram of how tool calling is used to provide to a language model similar to RAG.
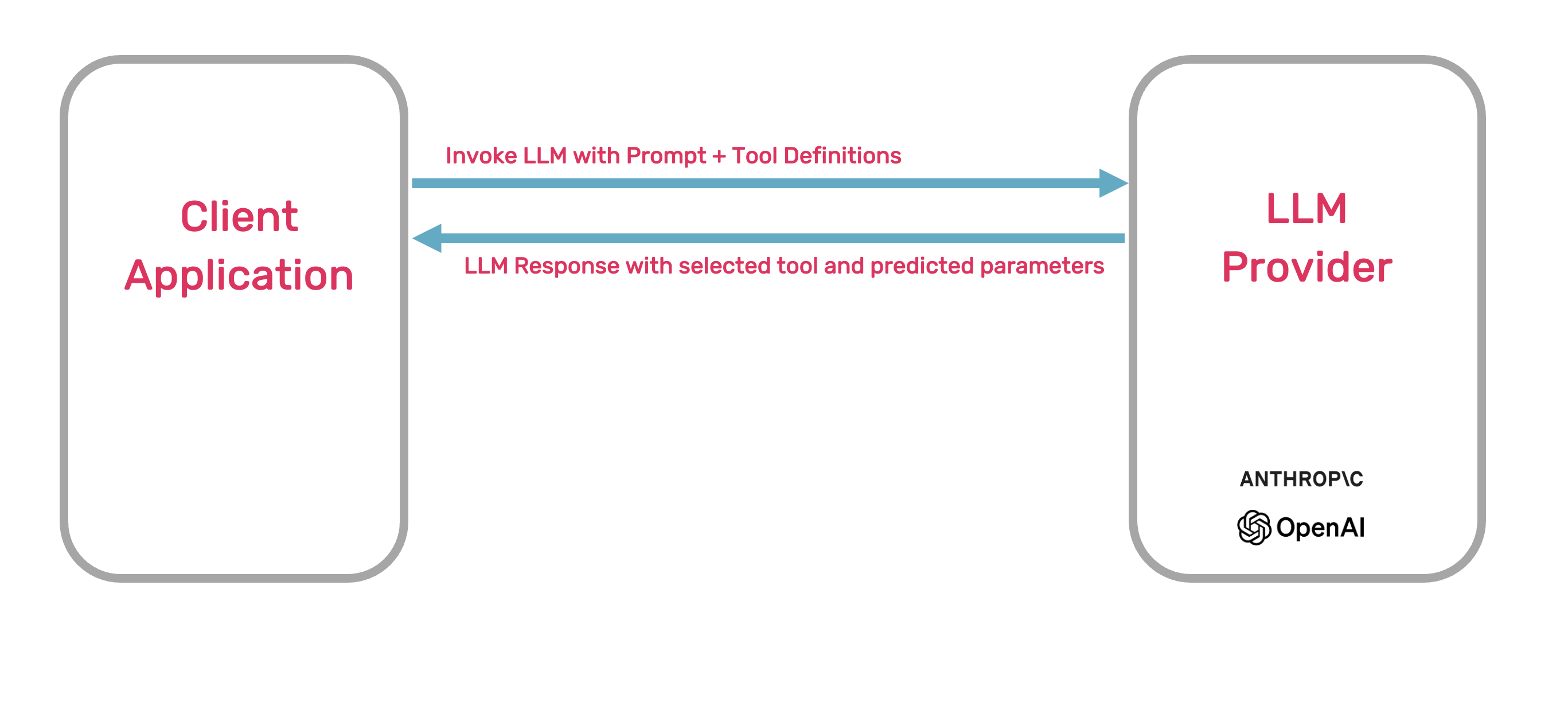
First, a language model is given a user’s request. The model then determines if it needs to use a to fulfill the request. If so, the model selects the appropriate tool from the tools listed in the request.
The model then predicts the parameters of that and passes these parameters back to the client application.
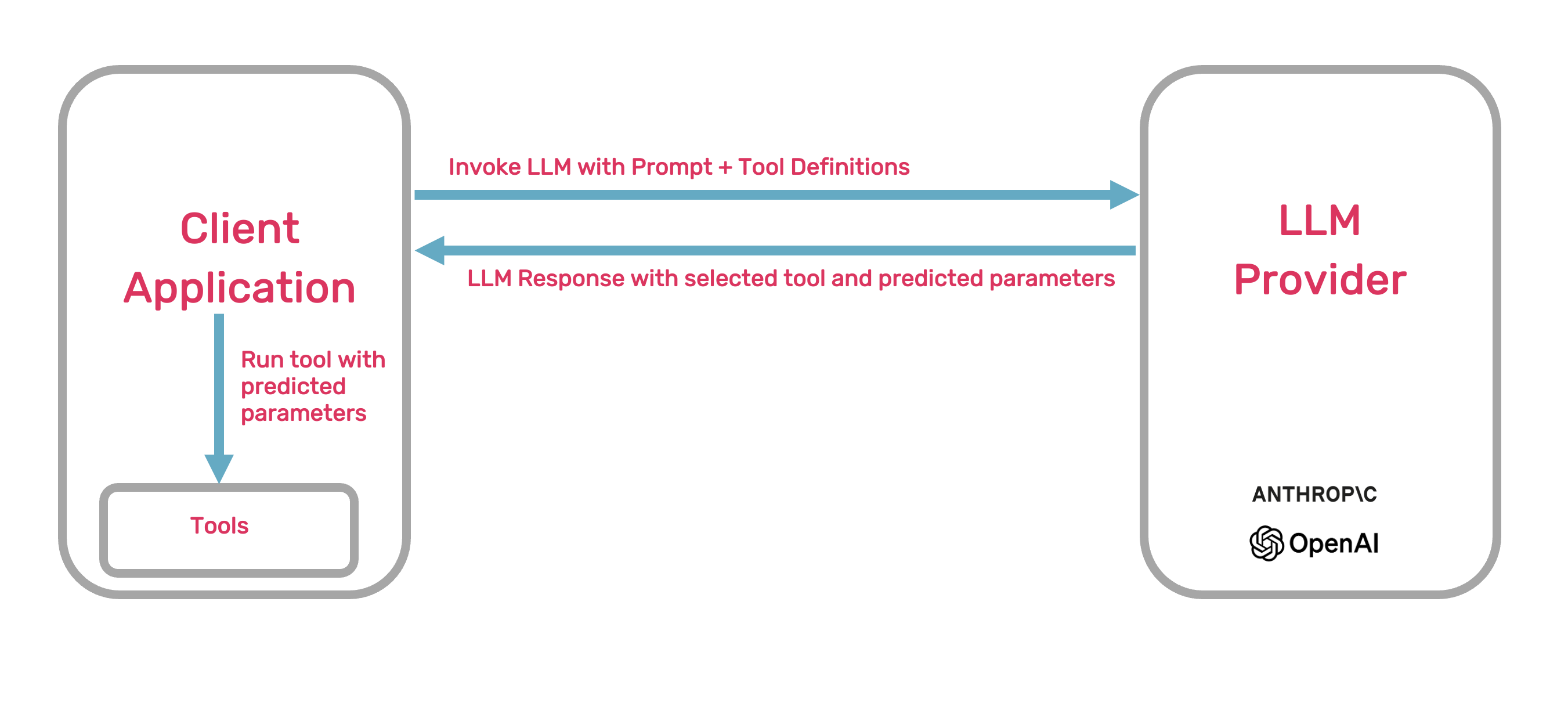
Now that the has been executed, the model can use the output to generate a response.
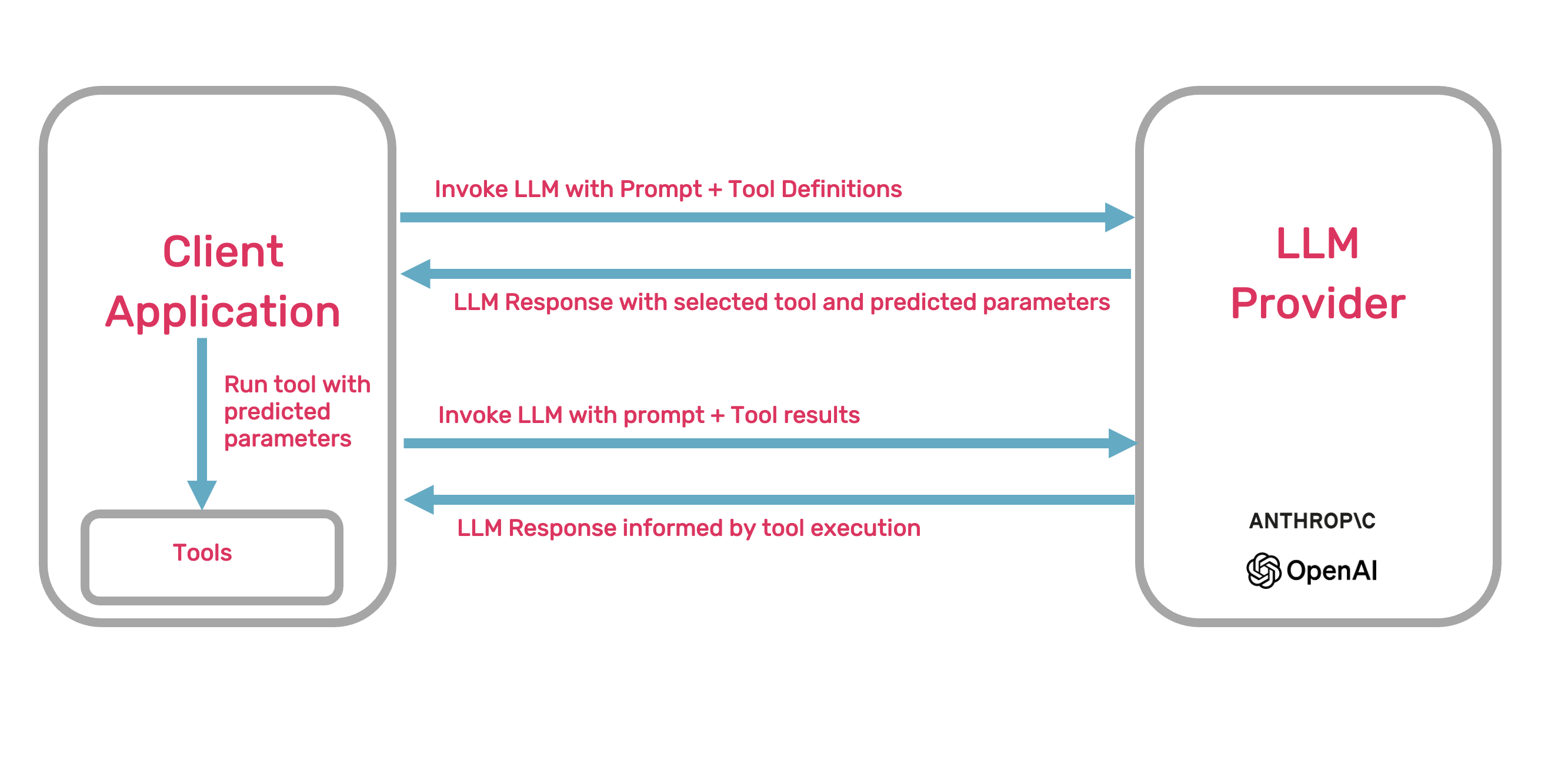
This process shows the general outline of the Augmented Generation (TAG) process at a high level.
Next steps
- Explore the MCP Servers available on Arcade
- Build your own custom MCP Server